
Motor testing is designed to check the integrity of an electric motor through the use of equipment that identifies potential issues within the motor. The main objective of motor testing is to reveal latent problems and to prevent unnecessary failure by evaluating static parameters like insulation, wire damage and electrical current leakage, as well as more dynamic parameters.
The insulating system of electrical machines is critical to reliability since an insulation failure may result in a system breakdown. Standard electrical tests currently required by regulations are unable to identify all types of failure. This is because many defects produce only partial discharges and these can only be identified using the partial discharge test method. This does not replace the standard tests but has to be performed in addition.
Partial discharge measurements allow detection ofall latent defects that could generate failures in e-motors, after short operating times. This is even more true for electric motors powered by Inverter – like electric vehicles – which, due to the inevitable voltage overshooting, causes more stress to the motor windings.
A typical fault that occurs, for instance, is when a wire touches the stack of the stator. If the enamel of the wire is scratched in the contact point with the stack, even the standard AC Hi-Pot test is can identify the fault. But, as commonly happens, if the wire is well insulated, the voltage applied during the AC Hi-Pot Test, even if quite high, may not be sufficient to break the remaining insulation material and this fault may not be identified. If the measurement of partial discharges is carried out at the same time as the AC Dielectric Strength Test then 100% of these defects are always identified and filtered.
The consequence of permanent partial discharges is a gradual yet continuous weakening of the functional parts of the insulation system. This leads to a complete breakdown and failure of the electric motor. That is why it’s important that there not be a partial discharge in the electric motor during operation. And, that is why the Marposs e.d.c. partial discharge testing method is valued by automotive manufacturers and Tier 1 suppliers.
The Marposs e.d.c. Partial Discharge Measurement System is based on capacitor coupling technology. As compared to antenna-type solutions normally applied in this market, the capacitor coupling technique is more sophisticated and less sensitive to external noise and, therefore, more suitable for applications in the production area. Since it does not use any external sensor, the coupling capacitor approach requires equipment that can detect the partial discharge just by connecting the terminals of the product under test with the same cables used to perform all other tests (winding resistance, AC High Pot tests, Surge Tests, etc.)
With the e.d.c. products, Marposs offers a complete range of solutions dedicated to the functional testing and the end-of-line testing of any type of electric motor, for in-line and off-line applications or for laboratory analysis and characterization.
Marposs provides customized inline and offline solutions for all electrical tests and detection of insulation problems at all stages of development and production of an e-motor and their components, such as:
- Stator Tester for production lines (wound or hairpin) that includes Partial Discharges measurements,
- Rotor Tester for all kinds of rotors (with permanent magnets, squirrel cage, wound),
- Automatic EoL Motor Tester (with Load/No-Load tests) for production, Dynamometer for motor Load Test & Life Simulation Cycles for laboratory,
- Advanced Windings and Insulation Quality Analysers for laboratory
As e-mobility continues to rapidly grow, vehicle manufacturers, as well as end-users, must be confident in the reliability of the vehicle functionality. As such, partial discharge measurement testing plays a crucial role as a standard testing process for electric motor manufacturers.
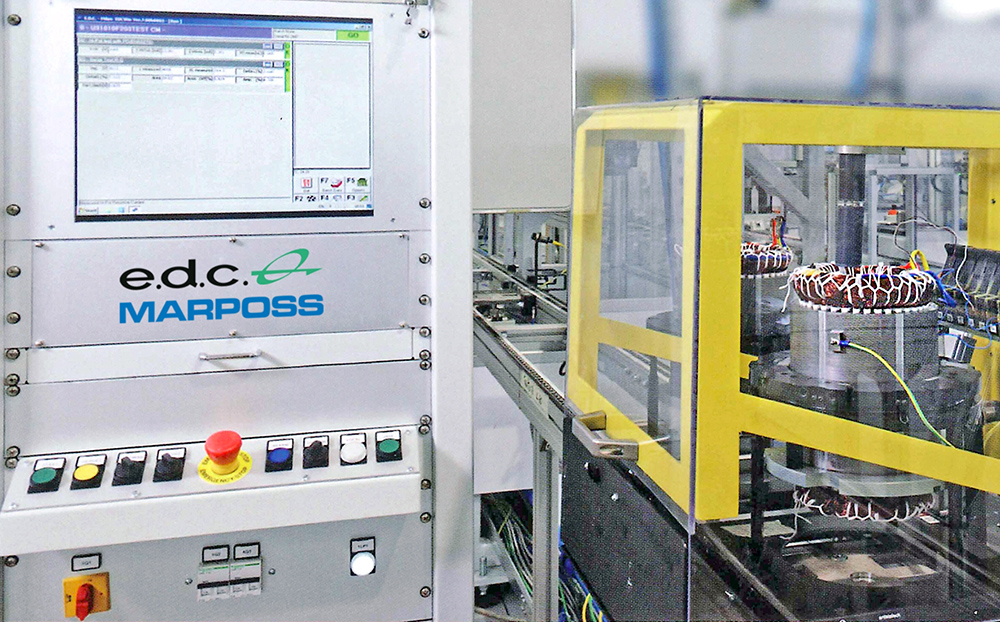

e.d.c. systems employ partical discharge measurement technology to identify 100% of latent defects and can be configured for stators, rotors, advanced windings, end of line tests.
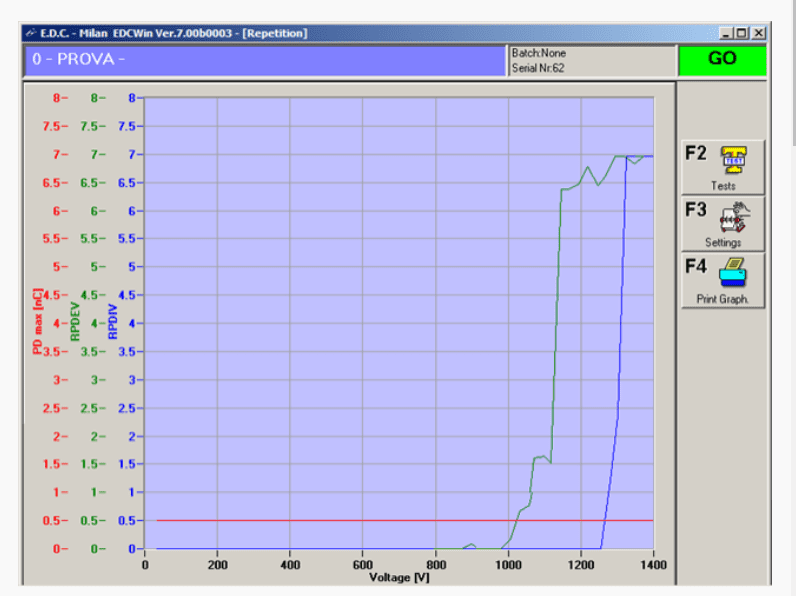
The e.d.c. partial discharge testing method is based on Capacitor Coupling technology that is more robust in relation to electromagnetic noise and consequently more suitable compared to Antenna method for the use in the production environment
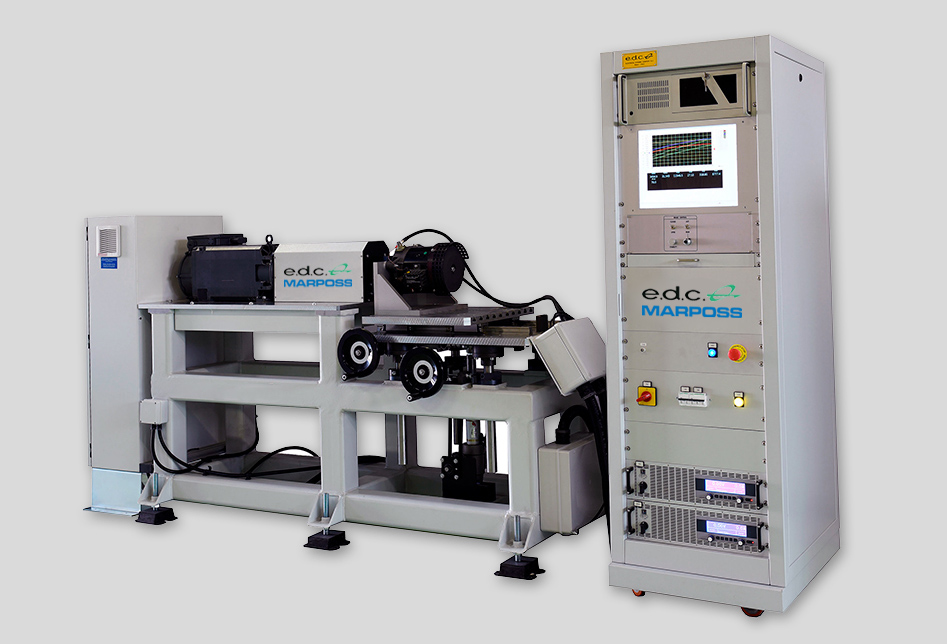

Customized EoL testing system for completely assembled e-motor to be integrated inline or offline for operator use. Design-to-order test benches are available for all kinds of rotors: Back EMF analysis for permanent magnets rotor, identification of defects of the cage bars for squirrel cage rotor.
Sponsored by Marposs.
from Charged EVs https://ift.tt/wNVKifx


No comments:
Post a Comment