
Ampere, the EV and software pure player from Renault, has entered into a joint development agreement (JDA) with Stratus Materials, a developer of cobalt-free lithium manganese oxide (LXMO) cathode active materials (CAM) for lithium-ion batteries.
The agreement marks the first step in evaluating the possibility of inserting Stratus Materials’ LXMO into Renault’s EV fleet and focuses on demonstrating the performance of the material in EV battery cells.
The technology will be tested in Ampere’s new Battery Cell Innovation Lab in Lardy, France.
LXMO technology offers high energy density, comparable to that of NMC batteries, and cost similar to that of LFP batteries. At the systems level, the combination of improved abuse tolerance and high energy density results in pack-level energy densities that are up to twice that of either NMC or LFP battery packs, according to Ampere. This promises lower-cost vehicles that offer longer range and better safety.
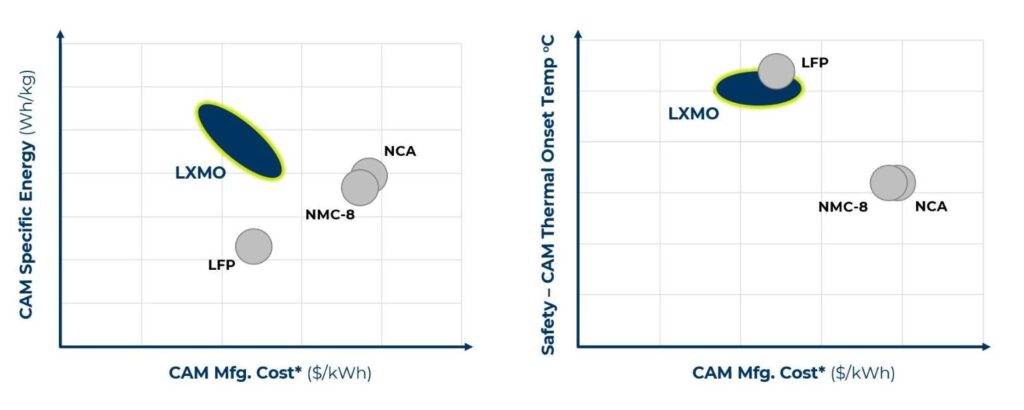
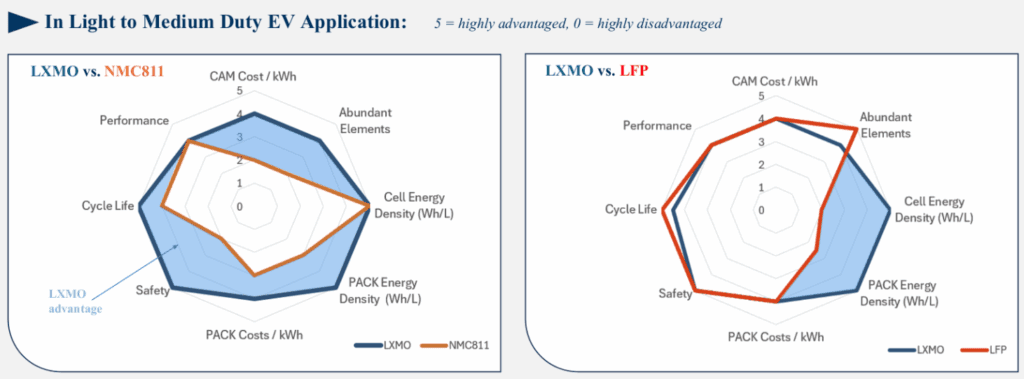
The collaboration is part of Ampere’s battery strategy to develop cobalt-free technology. The company has developed NMC and LFP technologies that will be used in Renault’s cars from 2026.
“Ampere is looking closely at high-energy cobalt-free materials because of their potential advantages compared to incumbent cathode materials. Stratus’s LXMOTM CAMs have gained Ampere’s attention because of their unique and compelling combination of performance, cost, safety, and cycle life,” said Nicolas Racquet, VP Vehicle & Powertrain Engineering, Ampere.
Source: Stratus Materials
from Charged EVs https://ift.tt/KwOEQNv


No comments:
Post a Comment